Free software: Java Toolkit for Desktop
This application is useful for Gasmet FTIR customers. It is based on Java and can run on all platforms, including Windows, Mac OS, and Linux:
- Humidity calculator
- Concentration calculator
- Molar mass calculator
- Sulfuric acid dew point
- Combustion calculator
- Spectral data
- Background correction
- Automatic processing of Gasmet result files (.txt)
- … and more
To get the software, please send us your request with full contact information and we will send you a download link
Humidity calculator
Humidity calculator provides a conversion of humidity values:
- absolute humidity
- relative humidity
- Partial pressure of water vapor
- Mass concentration of H 2 O
- Water dew point temperature
- Water vapor concentration
- Water vapor content / load
- Condensation pressure

Explanation:
- Absolute humidity = molar fraction / molar fraction of water = water vapor density = vapor density
- Partial pressure = partial pressure of water in air
- Load = mass of water vapor / mass of dry air
- Mass conc (actually standardized mass concentration) = mass of water / volume (relative to reference conditions, see above)
- Relative humidities > 100% are mathematically possible and are also displayed as such, but are physically irrelevant
This calculator is for guidance only, no guarantees. It is based on the ideal gas law.
Sulfuric acid dew point
Estimation of acid dew point (SO 2 in flue gas) of combustion gases
Sulfuric acid dew point calculator

Acid dew point calculator – The acid dew point (sulfuric acid condensation) is an important parameter for the design of a sampling system to reliably prevent condensation in your gas analyzer. This also leads to our recommendation to always keep cuvette temperatures in the GASMET gas analyzer more than 20°C above the water or acid dew point. This prevents damage. In most applications, a cuvette temperature of 180°C is sufficient.
The sulfuric acid dew point is comparable to the dew point of water. However, sulfuric acid is considered the condensate here. The carrier medium is usually exhaust gas/flue gas from the combustion of sulfur-containing fuels. The resulting components SO 2 and SO 3 react further with the water vapor in the exhaust gas to form sulfurous acid and sulfuric acid.
Please note that the quality of this estimate depends on the precision of the input parameters. The Okkes formula is used to calculate the sulfuric acid dew point.
This calculator is for guidance only and is not guaranteed.
Concentration calculator: ppm ↔ mg/m3
 Conversion of concentration quantities for gas analysis: Concentration quantities, content quantities
Conversion of concentration quantities for gas analysis: Concentration quantities, content quantities
Using this calculator, you can, for example, convert the units of a GT6000 Mobilis or GT5000 Terra , or change the display from mg/m3 to ppm. The calculation works with both the molar mass and the molecular formula.

Conversion of molar fractions (corresponds to volume concentrations) to standardized mass concentrations (note reference parameters) and back calculation.
The concentration can be expressed as a mass concentration (mg/m 3 ) or a volume concentration (cm 3 /m 3 ). For volume concentration, the unit used is ppm – parts per million. Thus, 1% = 10,000 ppm.
Please note : when entering the sum formulas
- Strict capitalization applies
- Brackets can be nested
Important to note: Standard condition according to DIN 1343 vs Normal Temperature and Pressure NTP vs standard conditions STP vs standard condition SATP?
The volume of a gaseous substance depends on pressure and temperature. Therefore, it is important to use correct pressure and temperature values. There are several definitions that define the standard state of a gaseous substance. The specified temperature is often 0°C, 15°C, 20°C, or 25°C, and the pressure is 1013.25 mbar or 1000.00 mbar. For example:
Standard condition according to DIN 1343:
In Germany, the standard conditions are regulated in DIN 1343 “Reference state, standard state, standard volume; terms, values”:
- Temperature T = 273.15 K corresponding to 0 °C
- Pressure p = 101325 Pa = 101325 N/m² = 1013.25 hPa = 101.325 kPa = 1013.25 mbar
Normal Temperature and Pressure NTP according to NIST:
Normal conditions, Normal Temperature and Pressure NTP according to National Institute of Standards and Technology NIST:
- Standard temperature T = 293.15 K corresponding to 20 °C (analogous to STP)
- Standard pressure p = 101300 Pa = 1013 hPa = 101.3 kPa = 1.013 bar
Standard conditions according to IUPAC, STP:
STP stands for “Standard Temperature and Pressure”, according to the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry IUPAC:
- Standard temperature / standard room temperature T = 273.15 K corresponding to 0 °C
- Standard pressure p = 100000 Pa = 1000 hPa = 100.0 kPa = 1.000 bar
Standard state / standard (room) conditions according to IUPAC, SATP:
SATP stands for “Standard Ambient Temperature and Pressure”, according to the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry IUPAC:
- Standard temperature / standard room temperature T = 298.15 K corresponding to 25 °C
- Standard pressure p = 100000 Pa = 1000 hPa = 100.0 kPa = 1.000 bar
| 1 ppm –> mg/m3 | DIN 1343 | NTP | STP | SATP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T=0°C | T=20°C | T=0°C | T=25°C | |
| p=1013 mbar | p=1013 | p=1000 | p=1000 | |
| Sulfur dioxide SO2 | 2.86 mg/m3 | 2.66 | 2.82 | 2.58 |
| Carbon monoxide CO | 1.25 mg/m3 | 1.16 | 1.23 | 1.13 |
| Carbon dioxide CO2 | 1.96 mg/m3 | 1.83 | 1.94 | 1.78 |
| Nitric oxide NO | 1.34 mg/m3 | 1.25 | 1.32 | 1.21 |
| NO as NO2 | 2.05 mg/m3 | 1.91 | 2.03 | 1.86 |
| Nitrogen dioxide NO2 | 2.05 mg/m3 | 1.91 | 2.03 | 1.86 |
| Hydrogen chloride HCl | 1.63 mg/m3 | 1.52 | 1.61 | 1.47 |
| Ammonia NH3 | 0.76 mg/m3 | 0.71 | 0.75 | 0.69 |
| Hydrogen fluoride HF | 0.89 mg/m3 | 0.83 | 0.88 | 0.81 |
| Ozone O3 | 2.14 mg/m3 | 1.99 | 2.11 | 1.94 |
| Formaldehyde CH2O | 1.34 mg/m3 | 1.25 | 1.32 | 1.21 |
| Sulfuric acid H2SO4 | 4.37 mg/m3 | 4.08 | 4.32 | 3.96 |
This calculator is based on the ideal gas law. It’s well-suited for use with an FTIR gas analyzer.
Combustion calculator
Ratio of O 2 and CO 2 in flue gas:

The oxygen required for combustion is determined from the fuel-specific proportions of hydrogen, oxygen, and carbon. The remaining oxygen not consumed during combustion in the case of excess air is a measure of the combustion efficiency. A high CO2 content in the exhaust gas indicates that a lot of carbon is being burned. If too much combustion air is supplied, the carbon dioxide content decreases and the oxygen content increases.
With clean combustion, the CO2 measurement or, conversely, the O2 measurement can be used to estimate the other value. For moist gases, the water vapor content must also be known. A water vapor value of zero provides the O2 concentration relative to the dry flue gas.
This calculator is for guidance only, no guarantees. It is based on the ideal gas law.
Molar mass calculator
Calculating the molar mass from the molecular formula:
- Strict capitalization applies
- Brackets can be nested

This calculator includes the following elements and atomic mass:
The molar mass M of a substance is the proportionality factor between mass m and amount n: M = m/n. The SI unit is kg/mol; in chemistry, g/mol is common.
| Element name | symbol | atomic number | atomic mass |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen (Hydrogenium) | H | 1 | 1.00794 |
| helium | Hey | 2 | 4.002602 |
| lithium | Li | 3 | 6,941 |
| beryllium | Be | 4 | 9.012182 |
| boron | B | 5 | 10,811 |
| Carbon (Carbonium) | C | 6 | 12,011 |
| Nitrogen (Nitrogenium) | N | 7 | 14.00674 |
| Oxygen (Oxygenium) | O | 8 | 15.9994 |
| fluorine | F | 9 | 18.9984032 |
| Neon | No | 10 | 20,1797 |
| sodium | N/a | 11 | 22.989768 |
| magnesium | Mg | 12 | 24,305 |
| aluminum | Al | 13 | 26.981539 |
| Silicon | Si | 14 | 28.0855 |
| phosphorus | P | 15 | 30.973762 |
| Sulfur (Sulpur) | S | 16 | 32,066 |
| chlorine | Cl | 17 | 35.4527 |
| argon | Ar | 18 | 39,948 |
| potassium | K | 19 | 39.0983 |
| Calcium | Ca | 20 | 40,078 |
| Scandium | Sc | 21 | 44.95591 |
| titanium | Ti | 22 | 47.88 |
| Vanadium | V | 23 | 50.9415 |
| chrome | Cr | 24 | 51.9961 |
| manganese | Mn | 25 | 54.93805 |
| Iron (Ferrum) | Fe | 26 | 55,847 |
| Cobalt | Co | 27 | 58.9332 |
| nickel | Ni | 28 | 58.69 |
| Copper (Cuprum) | Cu | 29 | 63,546 |
| zinc | Zn | 30 | 65.39 |
| gallium | Ga | 31 | 69,723 |
| Germanium | Ge | 32 | 72.61 |
| arsenic | Ace | 33 | 74.92159 |
| selenium | See | 34 | 78.96 |
| bromine | Br | 35 | 79,904 |
| krypton | Kr | 36 | 83.8 |
| Rubidium | Rb | 37 | 85.4678 |
| strontium | Sr | 38 | 87.62 |
| yttrium | Y | 39 | 88.90585 |
| Zirconium | Zr | 40 | 91,224 |
| niobium | Nb | 41 | 92.90638 |
| molybdenum | Mon | 42 | 95.94 |
| Technetium | Tc | 43 | 98.9063 |
| Ruthenium | Ru | 44 | 101.07 |
| Rhodium | Rh | 45 | 102.9055 |
| palladium | Pd | 46 | 106.42 |
| Silver (Argentum) | Ag | 47 | 107.8682 |
| cadmium | CD | 48 | 112,411 |
| Indium | In | 49 | 114.82 |
| Tin (Stannum) | Sn | 50 | 118.71 |
| Antimony (Stibium) | Sb | 51 | 121.75 |
| Tellur | The | 52 | 127.6 |
| Iodine | I | 53 | 126.90447 |
| xenon | Xe | 54 | 131.29 |
| Caesium | Cs | 55 | 132.90543 |
| barium | Ba | 56 | 137,327 |
| Lanthan | La | 57 | 138.9055 |
| cerium | Ce | 58 | 140,115 |
| Praseodym | Pr | 59 | 140.90765 |
| Neodym | Nd | 60 | 144.24 |
| promethium | PM | 61 | 146.9151 |
| Samarium | Sm | 62 | 150.36 |
| Europium | Eu | 63 | 151,965 |
| Gadolinium | Gd | 64 | 157.25 |
| Terbium | Tb | 65 | 158.92534 |
| Dysprosium | Dy | 66 | 162.5 |
| holmium | Ho | 67 | 164.93032 |
| Erbium | He | 68 | 167.26 |
| Thulium | Tm | 69 | 168.93421 |
| ytterbium | Yb | 70 | 173.04 |
| lutetium | Lu | 71 | 174,967 |
| hafnium | Hf | 72 | 178.49 |
| Tantal | Ta | 73 | 180.9479 |
| tungsten | W | 74 | 183.85 |
| rhenium | re | 75 | 186,207 |
| osmium | Os | 76 | 190.2 |
| iridium | Your | 77 | 192.22 |
| platinum | Pt | 78 | 195.08 |
| Gold (Aurum) | Au | 79 | 196.96654 |
| Mercury (Hydrargyrum) | Hg | 80 | 200.59 |
| Thallium | Tl | 81 | 204.3833 |
| Lead (Plumbum) | Pb | 82 | 207.2 |
| Bismuth also: Wismut | Bi | 83 | 208.98037 |
| polonium | Po | 84 | 208.9824 |
| Astat | At | 85 | 209.9871 |
| radon | Rn | 86 | 222.0176 |
| Francium | Fri | 87 | 223.0197 |
| radium | Ra | 88 | 226.0254 |
| Actinium | Ac | 89 | 227.0278 |
| Thorium | Th | 90 | 232.0381 |
| Protactinium | Pa | 91 | 231.0359 |
| uranium | U | 92 | 238.0289 |
| neptunium | Np | 93 | 237.0482 |
| plutonium | Pu | 94 | 244.0642 |
| Americium | On | 95 | 243.0614 |
| Curium | Cm | 96 | 247.0703 |
| Berkelium | Bk | 97 | 247.0703 |
| Californium | Cf | 98 | 251.0796 |
| Einsteinium | It | 99 | 252.0829 |
| Fermium | FM | 100 | 257.0951 |
| Mendelevium | Md | 101 | 258.0986 |
| Nobelium | No | 102 | 259.1009 |
| lawrencium | Lr | 103 | 260.1053 |
| Rutherfordium | RF | 104 | 261.1087 |
| Dubnium | Db | 105 | 262.1138 |
| Seaborgium | Sg | 106 | 263.1182 |
| Bohrium | Bra | 107 | 262.1229 |
| Hassium | Hs | 108 | 265 |
| Meitnerium | Mt | 109 | 266 |
| Darmstadtium | Ds | 110 | 269 |
| Roentgenium | Rg | 111 | 272 |
| Copernicium | Cn | 112 | 277 |
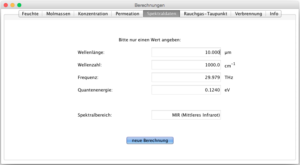
Spectral data
Conversion of spectral data or electromagnetic waves:
- Wavelength in µm.
- Wavenumber in cm -1
- Frequency in Hertz / THz
- Quantum energy in electron volts eV
This Java application and the calculators it contains are for guidance only and are not guaranteed.